Fine-tuning Llama 3.2 (1B, 3B) and Using It Locally with Llama Assistant 🌟
Access the notebook: https://github.com/vietanhdev/llama-assistant-train (opens in a new tab).
Hey there, AI enthusiasts! Ready to dive into the exciting world of Llama 3.2? This guide is your ticket to turning this powerful but pint-sized AI model into your very own customized assistant. We'll walk you through every step – from playing with pre-trained models to fine-tuning them to your specific needs, and deploying it locally with Llama Assistant.
You'll learn how to: 🚀
- 🦙 Get cozy with Llama 3.2's lightweight models.
- 🎓 Fine-tune Llama 3.2 with Unsloth performance boost + Monitoring with Weights & Biases.
- 🤗 Share your creation on Hugging Face Hub.
- 🏠 Bring your AI buddy home by converting it for local use with Llama Assistant.
Let's get started!
Getting Started
Acknowledgement
This guide is built based on training instructions from Unsloth. We extend our gratitude to the Unsloth team for providing valuable resources and insights that have made this fine-tuning process more efficient and accessible.
For more detailed information and the latest updates, please visit the official Unsloth documentation and repository.
Why Unsloth?
Unsloth is our tool of choice for fine-tuning Llama 3.2 due to its key advantages:
- 🚀 Speed: Makes fine-tuning 2x faster than traditional methods.
- 💾 Memory Efficiency: Uses 70% less memory, allowing for fine-tuning on less powerful hardware.
- 🎯 Precision: Maintains accuracy with no degradation in model performance.
- 🔧 Versatility: Works with various models including Llama-3, Mistral, Phi-3, and Gemma.
- 🔍 Optimization: Enables fine-tuning of larger models or use of larger batch sizes on the same hardware.
What is Weights & Biases?
Weights & Biases (wandb) is our tool of choice for monitoring the training process. It provides a comprehensive overview of the training process, including the loss, accuracy, and other metrics.
1. Install Dependencies
%%capture
!pip install unsloth
# Also get the latest nightly Unsloth!
!pip uninstall unsloth -y && pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir "unsloth[colab-new] @ git+https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth.git"
# Install Wandb for monitoring
!pip install wandb
# Login to Hugging Face
HUGGINGFACE_TOKEN = "<your-huggingface-token>"
from huggingface_hub import login
login(token = HUGGINGFACE_TOKEN)
# Login to Wandb
# Get API key from https://wandb.ai/settings#api
WANDB_API_KEY = "<your-wandb-api-key>"
import wandb
wandb.login(key = WANDB_API_KEY)
run = wandb.init(project = "Llama-3.2-1B-finetuned-FineTome-100k")from unsloth import FastLanguageModel
import torch
max_seq_length = 2048 # Choose any! We auto support RoPE Scaling internally!
dtype = None # None for auto detection. Float16 for Tesla T4, V100, Bfloat16 for Ampere+
load_in_4bit = True # Use 4bit quantization to reduce memory usage. Can be False.
# 4bit pre quantized models we support for 4x faster downloading + no OOMs.
fourbit_models = [
"unsloth/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-bnb-4bit", # Llama-3.1 2x faster
"unsloth/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-bnb-4bit",
"unsloth/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-bnb-4bit",
"unsloth/Meta-Llama-3.1-405B-bnb-4bit", # 4bit for 405b!
"unsloth/Mistral-Small-Instruct-2409", # Mistral 22b 2x faster!
"unsloth/mistral-7b-instruct-v0.3-bnb-4bit",
"unsloth/Phi-3.5-mini-instruct", # Phi-3.5 2x faster!
"unsloth/Phi-3-medium-4k-instruct",
"unsloth/gemma-2-9b-bnb-4bit",
"unsloth/gemma-2-27b-bnb-4bit", # Gemma 2x faster!
"unsloth/Llama-3.2-1B-bnb-4bit", # NEW! Llama 3.2 models
"unsloth/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-bnb-4bit",
"unsloth/Llama-3.2-3B-bnb-4bit",
"unsloth/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-bnb-4bit",
] # More models at https://huggingface.co/unsloth
model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(
model_name = "unsloth/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct", # or choose "unsloth/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct"
max_seq_length = max_seq_length,
dtype = dtype,
load_in_4bit = load_in_4bit,
)We now add LoRA adapters so we only need to update 1 to 10% of all parameters!
model = FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model(
model,
r = 32, # Choose any number > 0 ! Suggested 8, 16, 32, 64, 128
target_modules = ["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj",
"gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj",],
lora_alpha = 32,
lora_dropout = 0, # Supports any, but = 0 is optimized
bias = "none", # Supports any, but = "none" is optimized
# [NEW] "unsloth" uses 30% less VRAM, fits 2x larger batch sizes!
use_gradient_checkpointing = "unsloth", # True or "unsloth" for very long context
random_state = 3407,
use_rslora = False, # We support rank stabilized LoRA
loftq_config = None, # And LoftQ
)2. Data Preparation
We now use the Llama-3.2 format for conversation style finetunes. We use Maxime Labonne's FineTome-100k (opens in a new tab) dataset in ShareGPT style. But we convert it to HuggingFace's normal multiturn format ("role", "content") instead of ("from", "value")/ Llama-3 renders multi turn conversations like below:
<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>
Hello!<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
Hey there! How are you?<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>
I'm great thanks!<|eot_id|>from unsloth.chat_templates import get_chat_template
tokenizer = get_chat_template(
tokenizer,
chat_template = "llama-3.1",
)
def formatting_prompts_func(examples):
convos = examples["conversations"]
texts = [tokenizer.apply_chat_template(convo, tokenize = False, add_generation_prompt = False) for convo in convos]
return { "text" : texts, }
pass
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("mlabonne/FineTome-100k", split = "train")We now use standardize_sharegpt to convert ShareGPT style datasets into HuggingFace's generic format. This changes the dataset from looking like:
{"from": "system", "value": "You are an assistant"}
{"from": "human", "value": "What is 2+2?"}
{"from": "gpt", "value": "It's 4."}to
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an assistant"}
{"role": "user", "content": "What is 2+2?"}
{"role": "assistant", "content": "It's 4."}from unsloth.chat_templates import standardize_sharegpt
dataset = standardize_sharegpt(dataset)
dataset = dataset.map(formatting_prompts_func, batched = True,)We look at how the conversations are structured for item 5:
dataset[5]["conversations"]And we see how the chat template transformed these conversations.
[Notice] Llama 3.1 Instruct's default chat template default adds "Cutting Knowledge Date: December 2023\nToday Date: 26 July 2024", so do not be alarmed!
dataset[5]["text"]3. Train the model
Now let's use Huggingface TRL's SFTTrainer! More docs here: TRL SFT docs (opens in a new tab). We do 60 steps to speed things up, but you can set num_train_epochs=1 for a full run, and turn off max_steps=None. We also support TRL's DPOTrainer!
from trl import SFTTrainer
from transformers import TrainingArguments, DataCollatorForSeq2Seq
from unsloth import is_bfloat16_supported
trainer = SFTTrainer(
model = model,
tokenizer = tokenizer,
train_dataset = dataset,
dataset_text_field = "text",
max_seq_length = max_seq_length,
data_collator = DataCollatorForSeq2Seq(tokenizer = tokenizer),
dataset_num_proc = 2,
packing = False, # Can make training 5x faster for short sequences.
args = TrainingArguments(
per_device_train_batch_size = 4,
gradient_accumulation_steps = 4,
warmup_steps = 5,
num_train_epochs = 1, # Set this for 1 full training run.
# max_steps = 60,
learning_rate = 2e-4,
fp16 = not is_bfloat16_supported(),
bf16 = is_bfloat16_supported(),
logging_steps = 1,
optim = "adamw_8bit",
weight_decay = 0.01,
lr_scheduler_type = "linear",
seed = 3407,
output_dir = "outputs",
report_to="wandb"
),
)We also use Unsloth's train_on_completions method to only train on the assistant outputs and ignore the loss on the user's inputs.
from unsloth.chat_templates import train_on_responses_only
trainer = train_on_responses_only(
trainer,
instruction_part = "<|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>\n\n",
response_part = "<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>\n\n",
)We verify masking is actually done:
tokenizer.decode(trainer.train_dataset[5]["input_ids"])space = tokenizer(" ", add_special_tokens = False).input_ids[0]
tokenizer.decode([space if x == -100 else x for x in trainer.train_dataset[5]["labels"]])We can see the System and Instruction prompts are successfully masked!
#@title Show current memory stats
gpu_stats = torch.cuda.get_device_properties(0)
start_gpu_memory = round(torch.cuda.max_memory_reserved() / 1024 / 1024 / 1024, 3)
max_memory = round(gpu_stats.total_memory / 1024 / 1024 / 1024, 3)
print(f"GPU = {gpu_stats.name}. Max memory = {max_memory} GB.")
print(f"{start_gpu_memory} GB of memory reserved.")trainer_stats = trainer.train()
# Finish wandb run
# The detailed run history is generated when we finish the Weights & Biases run.
run.finish()#@title Show final memory and time stats
used_memory = round(torch.cuda.max_memory_reserved() / 1024 / 1024 / 1024, 3)
used_memory_for_lora = round(used_memory - start_gpu_memory, 3)
used_percentage = round(used_memory /max_memory*100, 3)
lora_percentage = round(used_memory_for_lora/max_memory*100, 3)
print(f"{trainer_stats.metrics['train_runtime']} seconds used for training.")
print(f"{round(trainer_stats.metrics['train_runtime']/60, 2)} minutes used for training.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory = {used_memory} GB.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory for training = {used_memory_for_lora} GB.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory % of max memory = {used_percentage} %.")
print(f"Peak reserved memory for training % of max memory = {lora_percentage} %.")4. Inference
Let's run the model! You can change the instruction and input - leave the output blank!
We use min_p = 0.1 and temperature = 1.5. Read this Tweet (opens in a new tab) for more information on why.
from unsloth.chat_templates import get_chat_template
tokenizer = get_chat_template(
tokenizer,
chat_template = "llama-3.1",
)
FastLanguageModel.for_inference(model) # Enable native 2x faster inference
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Continue the fibonnaci sequence: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8,"},
]
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize = True,
add_generation_prompt = True, # Must add for generation
return_tensors = "pt",
).to("cuda")
outputs = model.generate(input_ids = inputs, max_new_tokens = 64, use_cache = True,
temperature = 1.5, min_p = 0.1)
tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs)You can also use a TextStreamer for continuous inference - so you can see the generation token by token, instead of waiting the whole time!
FastLanguageModel.for_inference(model) # Enable native 2x faster inference
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Continue the fibonnaci sequence: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8,"},
]
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize = True,
add_generation_prompt = True, # Must add for generation
return_tensors = "pt",
).to("cuda")
from transformers import TextStreamer
text_streamer = TextStreamer(tokenizer, skip_prompt = True)
_ = model.generate(input_ids = inputs, streamer = text_streamer, max_new_tokens = 128,
use_cache = True, temperature = 1.5, min_p = 0.1)5. Save the model
To save the final model as LoRA adapters, either use Huggingface's push_to_hub for an online save or save_pretrained for a local save.
[NOTE] This ONLY saves the LoRA adapters, and not the full model. To save to 16bit or GGUF, scroll down!
model.save_pretrained("lora_model") # Local saving
tokenizer.save_pretrained("lora_model")
# model.push_to_hub("your_name/lora_model", token = "...") # Online saving
# tokenizer.push_to_hub("your_name/lora_model", token = "...") # Online savingNow if you want to load the LoRA adapters we just saved for inference, set False to True:
if False:
from unsloth import FastLanguageModel
model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(
model_name = "lora_model", # YOUR MODEL YOU USED FOR TRAINING
max_seq_length = max_seq_length,
dtype = dtype,
load_in_4bit = load_in_4bit,
)
FastLanguageModel.for_inference(model) # Enable native 2x faster inference
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Describe a tall tower in the capital of France."},
]
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize = True,
add_generation_prompt = True, # Must add for generation
return_tensors = "pt",
).to("cuda")
from transformers import TextStreamer
text_streamer = TextStreamer(tokenizer, skip_prompt = True)
_ = model.generate(input_ids = inputs, streamer = text_streamer, max_new_tokens = 128,
use_cache = True, temperature = 1.5, min_p = 0.1)Saving to float16 for VLLM
We also support saving to float16 directly. Select merged_16bit for float16 or merged_4bit for int4. We also allow lora adapters as a fallback. Use push_to_hub_merged to upload to your Hugging Face account! You can go to https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens (opens in a new tab) for your personal tokens.
# Update the model name to your desired name and add your Hugging Face username
# Merge to 16bit
if True: model.save_pretrained_merged("llama-3.2-1B-finetuned-finetome-100k-fp16", tokenizer, save_method = "merged_16bit")
if True: model.push_to_hub_merged("vietanhdev/llama-3.2-1B-finetuned-finetome-100k-fp16", tokenizer, save_method = "merged_16bit")
# Merge to 4bit
if False: model.save_pretrained_merged("model", tokenizer, save_method = "merged_4bit",)
if False: model.push_to_hub_merged("hf/model", tokenizer, save_method = "merged_4bit")
# Just LoRA adapters
if False: model.save_pretrained_merged("model", tokenizer, save_method = "lora",)
if False: model.push_to_hub_merged("hf/model", tokenizer, save_method = "lora")6. Convert to GGUF - Use with Llama Assistant
To save to GGUF / llama.cpp, we support it natively now! We clone llama.cpp and we default save it to q8_0. We allow all methods like q4_k_m. Use save_pretrained_gguf for local saving and push_to_hub_gguf for uploading to HF.
Some supported quant methods (full list on our Wiki page (opens in a new tab)):
q4_k_m- Recommended. Uses Q6_K for half of the attention.wv and feed_forward.w2 tensors, else Q4_K.q5_k_m- Recommended. Uses Q6_K for half of the attention.wv and feed_forward.w2 tensors, else Q5_K.
# Update the model name to your desired name and add your Hugging Face username
base_name = "llama-3.2-1B-finetuned-finetome-100k-gguf"
# Save to multiple GGUF options - much faster if you want multiple!
if True:
model.push_to_hub_gguf(
"vietanhdev/llama-3.2-1B-finetuned-finetome-100k-gguf", # Change hf to your username!
tokenizer,
quantization_method = ["q4_k_m", "q8_0", "q5_k_m",],
)Another way to convert to GGUF is to use ggml-org/gguf-my-repo (opens in a new tab) to convert with a GUI.
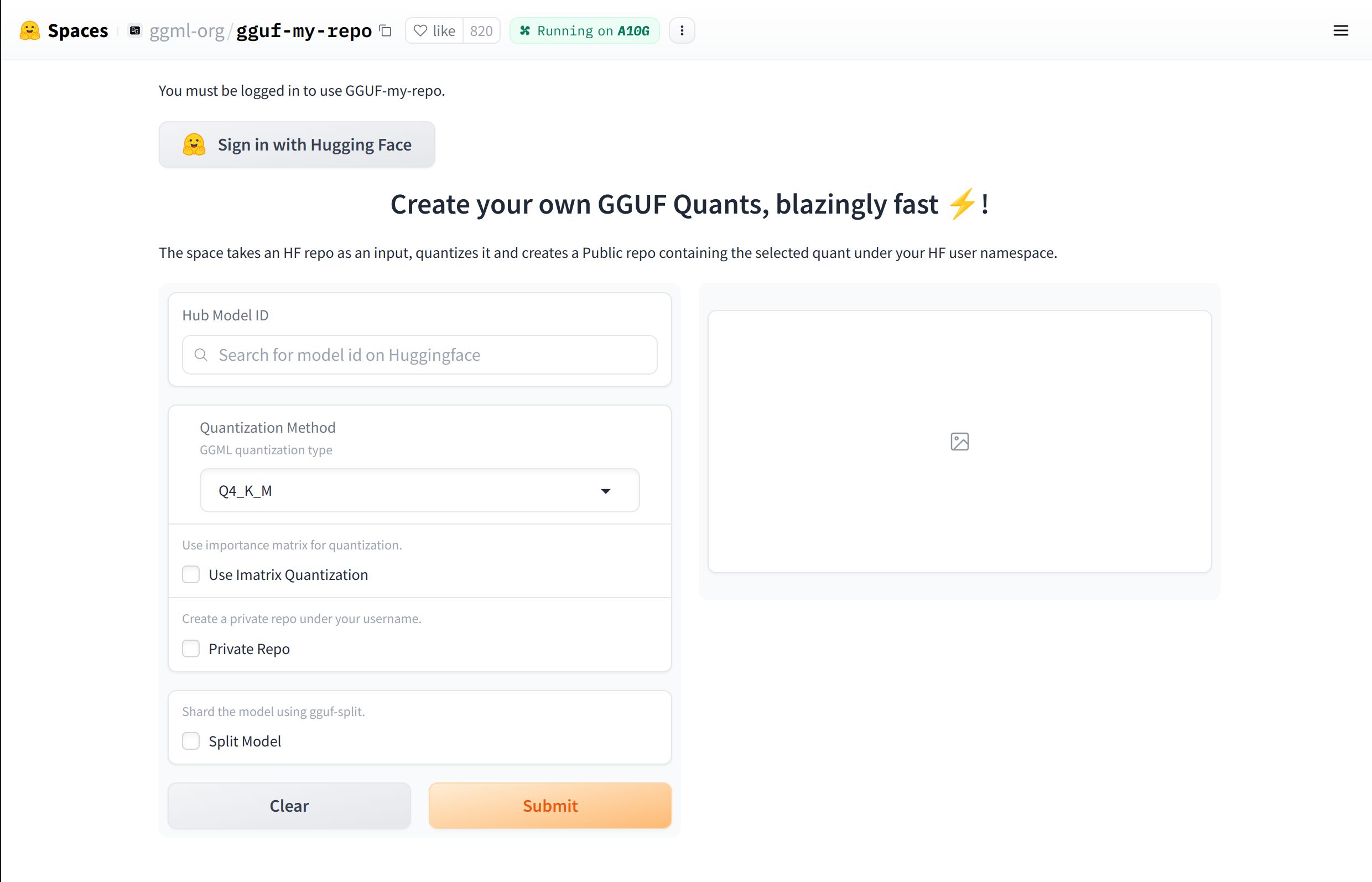
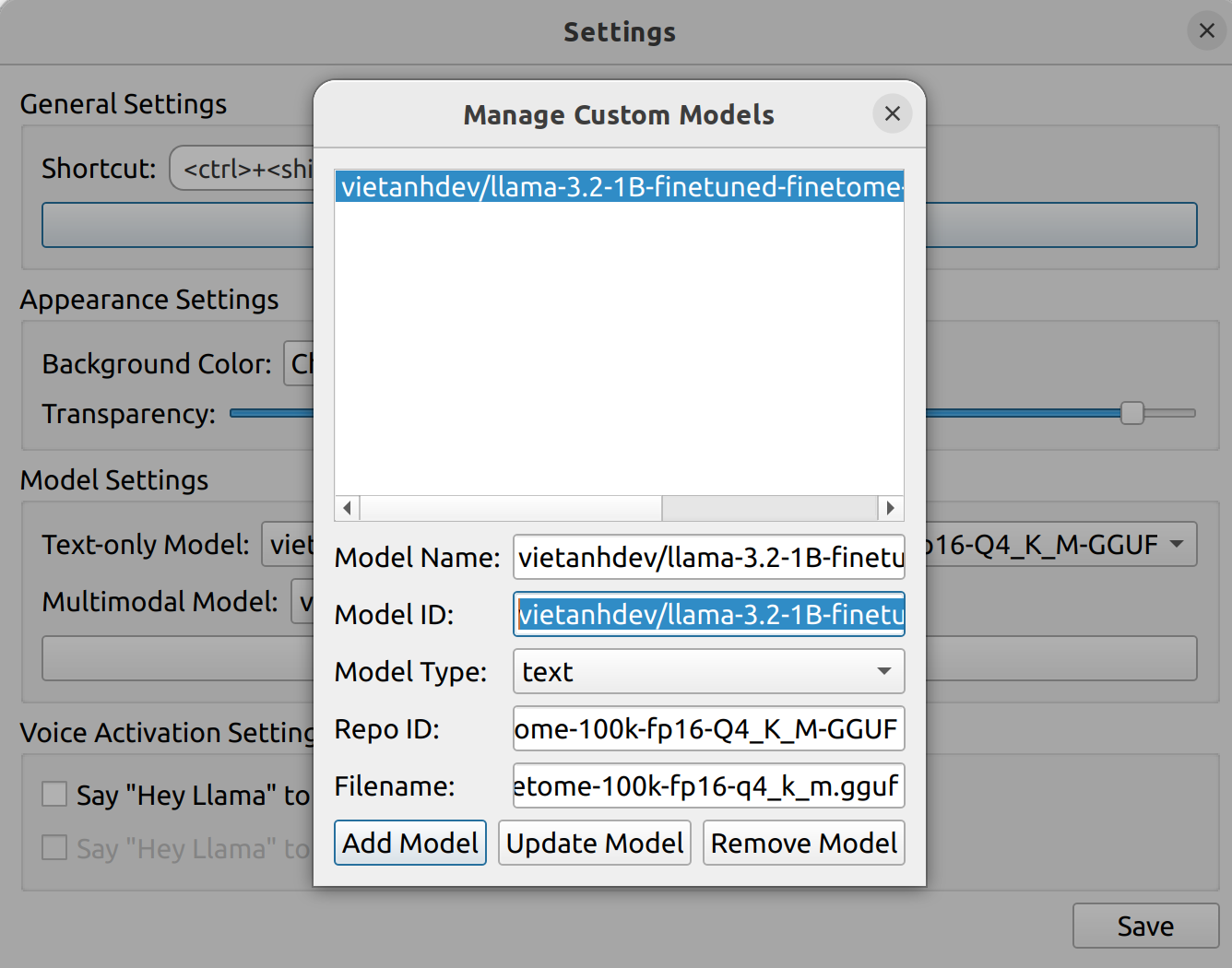
Load the model with Llama Assistant
You can load the model with Llama Assistant by using Custom Models feature in the Settings UI.
Access the notebook: https://github.com/vietanhdev/llama-assistant-train (opens in a new tab).